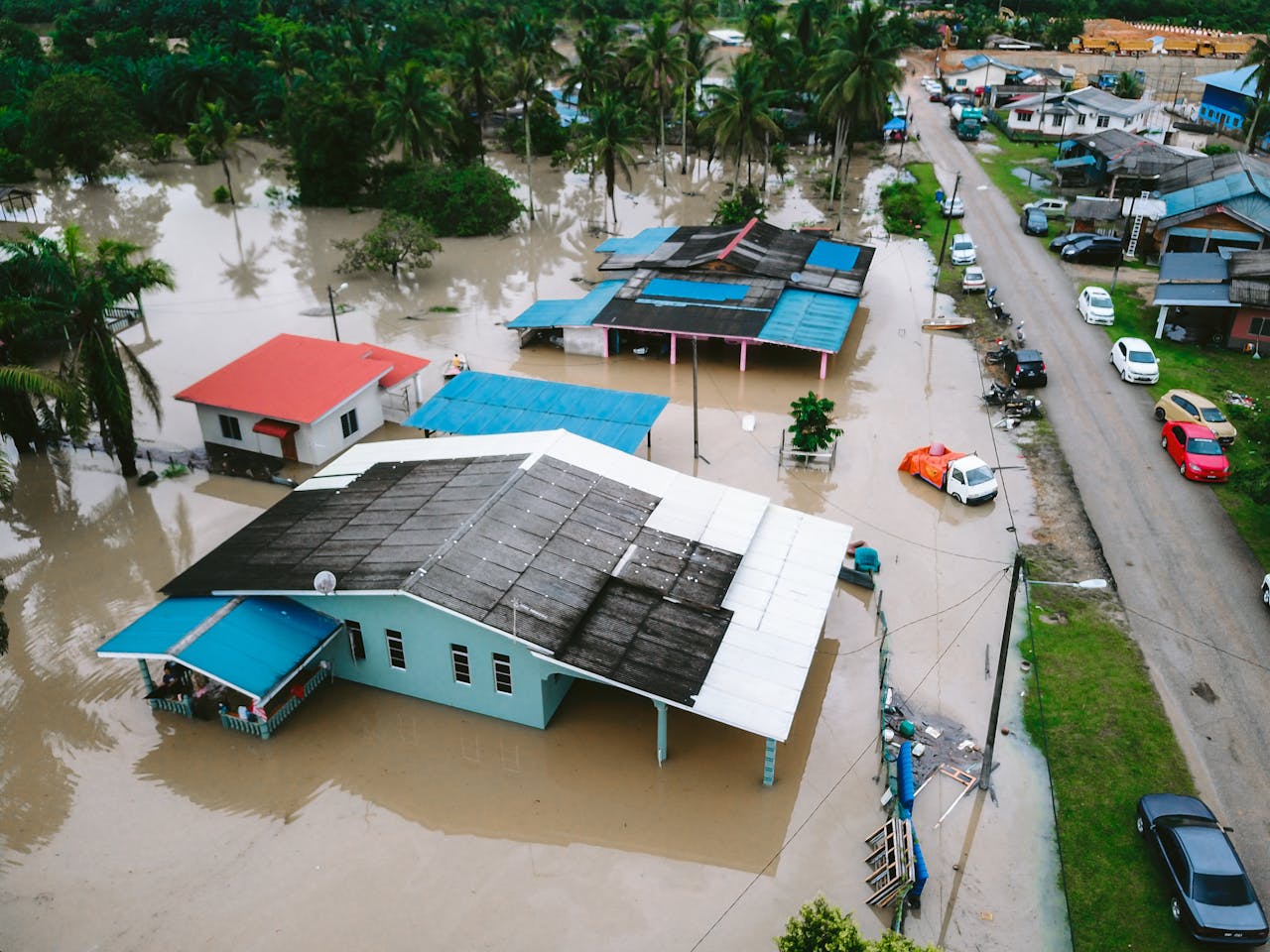

Best Standby Generator Placement for Homes in Flood-Prone Areas
Published: November 18, 2024 | By Thomas Morgan
Best Standby Generator Placement for Homes in Flood-Prone Areas
Published: May 12, 2025 | By Robert Chen, Flood Mitigation Specialist
For homeowners in flood-prone regions, standby generators represent a critical lifeline during emergencies—particularly when flooding and power outages coincide. Yet paradoxically, the very conditions that make generators essential also create significant risks to the generators themselves.
Improperly placed generators in flood zones can become damaged or completely destroyed during high water events, leaving homes without power precisely when it's most needed. Even worse, flooded generators can create dangerous electrical and environmental hazards. To select the properly sized generator for your flood-prone home, use our Generator Sizing Calculator to ensure adequate power while considering flood-safe installation strategies.
This comprehensive guide explores strategic placement, protective measures, and regulatory considerations for standby generators in flood-prone areas, helping you ensure your backup power system remains functional and safe even during severe flooding events.
Key Takeaway: Proper standby generator placement in flood-prone areas requires elevating the unit at least 1-2 feet above the 100-year flood level (or local flood protection elevation requirements), securing it against buoyancy forces, protecting electrical connections, and ensuring proper drainage. This strategic approach significantly increases the likelihood your generator will remain operational during flooding—when backup power is most critical.
Understanding Flood Risks to Generators

Before exploring placement strategies, it's essential to understand the specific ways flooding threatens standby generator systems:
Direct Water Damage Risks
- Electrical system shorting and component failure
- Control panel damage from water intrusion
- Engine damage from water entering intake systems
- Contamination of fuel systems
- Corrosion of critical components
- Insulation breakdown in windings and electrical systems
- Lubricant contamination and dilution
Secondary Flood Hazards
- Foundation undermining from erosion
- Floating/displacement from buoyancy forces
- Debris impact damage during flooding
- Electrical ground faults creating shock hazards
- Mold and microbial growth after water recedes
- Fuel leakage creating environmental hazards
- Mud and sediment fouling in cooling systems
Even generators that survive initial flooding often require expensive repairs or complete replacement. According to insurance industry data, over 60% of generators in flood-affected areas require significant servicing or replacement after major flooding events—primarily due to poor initial placement decisions.
Generator Elevation: The Foundation of Flood Protection

The single most important flood protection strategy is proper elevation of your standby generator. Here's how to approach this critical decision:
1. Determining Appropriate Elevation Height
Your generator should be elevated based on these key references:
- Base Flood Elevation (BFE): The elevation floodwaters are expected to reach during a 100-year flood
- Design Flood Elevation (DFE): BFE plus a safety factor (freeboard) required by local codes
- Historical high water marks in your specific location
- Local floodplain ordinances which may specify minimum heights
- Future flood projections accounting for climate change
As a general rule, your generator should be installed at least 1-2 feet above the highest of these reference points, creating a crucial margin of safety for unexpected flood levels.
Finding Your BFE:
- FEMA Flood Insurance Rate Maps (FIRMs)
- Local building/zoning departments
- Flood elevation certificates
- Professional land surveyors
- FEMA's Map Service Center online
2. Elevation Methods for Standby Generators
Several proven methods exist for elevating generators in flood zones:
- Raised concrete pads: Solid concrete foundations elevated above flood levels
- Engineered platforms: Steel or reinforced structures designed for specific flood loads
- Composite pedestals: Specialized flood-resistant platforms with integrated conduit channels
- Wall-mounted brackets: For smaller units where wall structure permits
- Rooftop placement: For buildings with appropriate structural capacity
- Natural elevation advantage: Utilizing existing high points on the property
Each approach has specific advantages and limitations based on generator size, property layout, and flood characteristics.
Cost Implications:
- Basic raised pad: $800-$1,500
- Engineered platform: $2,000-$5,000
- Composite pedestal: $1,500-$3,000
- Wall mounting: $1,200-$2,500
- Rooftop installation: $3,000-$7,000
3. Critical Design Considerations for Elevated Platforms
Elevated generator platforms must be designed to address multiple challenges:
- Buoyancy resistance: Anchoring systems to prevent floating during floods
- Hydrodynamic forces: Ability to withstand flowing water pressure
- Debris impact protection: Reinforcement against floating objects
- Vibration isolation: Dampening systems to prevent structure fatigue
- Maintenance accessibility: Safe access for servicing when needed
- Weight bearing capacity: Support for generator plus fuel systems
- Erosion prevention: Scour protection around foundation elements
Engineering Requirements:
- Professional engineering review typically required
- Specific flood zone building codes apply
- Additional permits often necessary
- May require geotechnical assessment
Case Study: Elevated Generator Performance During Hurricane Flooding
During Hurricane Ida in 2021, a coastal Louisiana community experienced severe flooding that reached 4.5 feet above ground level. A comparative analysis of generator outcomes in the community revealed:
- Ground-level generators: 96% suffered catastrophic damage requiring complete replacement
- Generators elevated 1 foot above BFE: 24% required significant repairs but remained operational
- Generators elevated 2+ feet above BFE: Over 90% remained fully operational after floodwaters receded
Source: Louisiana State University Hurricane Center Post-Event Assessment Report, 2022
Strategic Placement Beyond Elevation

While elevation is essential, other location factors significantly impact generator performance and safety during flooding:
1. Flow Dynamics Consideration
Floodwaters rarely rise statically; they flow with considerable force:
- Position generators perpendicular to potential flood flow direction, minimizing water resistance
- Avoid placement in natural drainage channels or water pathways
- Consider protective walls or barriers upstream of the generator
- Place on the downstream side of structures when possible
- In coastal areas, account for wave action and storm surge directions
Proper orientation can dramatically reduce hydrodynamic forces on your generator platform during flooding events.
Expert Insight:
"Just 2 feet of flowing floodwater can exert over 500 pounds of lateral force on a generator enclosure. Strategic positioning can reduce this force by 30-40%."
- Dr. Helen Martinez, Hydraulic Engineering Specialist
2. Debris Exposure Management
Floating debris is a major cause of generator damage during floods:
- Avoid placement downstream from structures likely to break apart
- Consider natural barriers like strategic landscaping
- Install bollards or concrete barriers to deflect large debris
- Position away from trees that may drop limbs during storms
- Use reinforced generator enclosures in high-debris areas
Even properly elevated generators can be severely damaged by large debris impacts during flooding.
Protective Options:
- Debris deflection walls
- Reinforced generator housing
- Sacrificial barriers
- Strategic landscaping
3. Erosion and Soil Stability Factors
Floodwaters can undermine foundations through erosion:
- Avoid placement on fill soil without proper compaction
- Incorporate scour protection around foundation supports
- Use erosion control measures like riprap or vegetation
- Consider deep foundations for areas with significant erosion potential
- Implement French drains and proper water management around the generator
Soil analysis should be conducted before finalizing generator placement in areas with unknown soil stability.
Signs of Concern:
- Previous erosion on property
- Sandy or loose soil composition
- Steep slopes nearby
- Evidence of soil settlement
- High groundwater table
4. Utility Connection Management
Critical connections to your generator must be flood-resistant:
- Route electrical conduits from above flood levels when possible
- Use waterproof conduit and connections rated for submersion
- Elevate fuel lines and connections above flood levels
- Install check valves and automatic shutoffs for fuel systems
- Position control panels and transfer switches above flood elevation
- Consider quick-disconnect systems for rapid pre-flood preparation
Even properly elevated generators often fail due to submerged connections and utility feeds.
Key Protection Points:
- Electrical conduit entries
- Fuel line connections
- Control cable routing
- Communications links
- Exhaust and intake systems
Placement Considerations by Generator Type
Different generator types have unique requirements and vulnerabilities in flood-prone areas:
| Generator Type | Special Flood Considerations | Recommended Adaptations |
|---|---|---|
| Air-Cooled Standby (8-24kW) |
|
|
| Liquid-Cooled Standby (20-150kW) |
|
|
| Diesel Standby Generators |
|
|
| Natural Gas Standby Generators |
|
|
When selecting a generator for a flood-prone location, these specific vulnerabilities should influence both your generator type selection and placement strategy. Consult with specialists familiar with your specific generator model for customized recommendations.
Regulatory Compliance for Flood Zone Generator Placement

Installing generators in flood-prone areas involves navigating various regulations and permit requirements:
FEMA and Floodplain Regulations
- National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) requirements
- Base Flood Elevation (BFE) compliance standards
- Substantial improvement considerations
- Flood-resistant materials specifications
- Documentation and certification requirements
- Community Rating System (CRS) participation benefits
Important: Non-compliance can affect flood insurance eligibility and rates, as well as create liability issues.
Local Code Requirements
- Local floodplain management ordinances
- Building code requirements for mechanical equipment
- Electrical code provisions for flood-prone areas
- Environmental protection regulations
- Noise ordinance compliance
- Zoning and setback requirements
Note: Local requirements often exceed federal standards and should be verified early in the planning process.
Required Permits and Documentation
Generator installation in flood zones typically requires these specific permits and documents:
- Floodplain Development Permit
Required for any development within mapped flood zones, including generator installation
- Electrical Permit
With specific notations regarding flood zone considerations and requirements
- Mechanical/Plumbing Permit
For fuel line connections and related systems
- Elevation Certificate
Documenting the elevation of the generator relative to BFE
- Structural Engineering Certification
Verifying the elevated platform meets flood resistance requirements
- Environmental Compliance Documentation
Particularly for diesel units with fuel storage considerations
- Homeowners Association Approval
If applicable to your property
Working with installers and engineers familiar with flood zone requirements can significantly streamline this process and ensure compliance.
Advanced Flood Protection Measures

For properties in severe flood zones or where conventional elevation isn't feasible, these specialized approaches provide additional protection:
1. Flood Barriers and Dry Floodproofing
Physical barriers can protect generators even in flood-prone locations:
- Permanent flood walls surrounding the generator
- Deployable flood barriers for pre-storm protection
- Custom-fitted generator shields with waterproof seals
- Submersible-rated generator enclosures
- Integrated pumping systems to remove water intrusion
These solutions are particularly valuable for properties where sufficient elevation isn't possible due to space or aesthetic constraints.
Effectiveness Limits:
Dry floodproofing is typically effective up to 3 feet of water depth. Beyond this, hydrostatic pressure becomes too great for most barrier systems.
2. Quick Disconnect Systems
For areas with advance flood warnings, rapid disconnection capabilities offer protection:
- Quick-connect electrical couplings for fast disconnection
- Rapid-disconnect fuel line systems
- Modular mounting systems allowing generator relocation
- Pre-wired secondary connection points at higher elevations
- Portable generator receptacles at elevated locations
- Weather-sealed connection enclosures for recommissioning
These systems allow homeowners to protect generators by disconnecting critical components before floodwaters rise, then quickly reconnect after the threat passes.
Implementation Cost:
Quick-disconnect systems typically add $1,200-$3,500 to installation costs but can save tens of thousands in potential flood damage.
3. Remote Generator Placement
Locating generators away from the main structure on higher ground:
- Natural elevation advantages on the property
- Long-run electrical connections to elevated locations
- Secondary structures specifically designed for generator housing
- Shared generator locations for multiple properties
- Ridge or hillside placement with appropriate weather protection
While involving higher initial costs for electrical runs, remote placement can dramatically reduce flood risks in properties with significant elevation differences.
Distance Limitations:
Generator performance can be affected by voltage drop in long cable runs. Professional electrical design is essential for distances exceeding 100 feet.
4. Submersible-Rated Equipment
Specialized equipment designed to withstand temporary submersion:
- Marine-grade generator components
- Sealed submersible transfer switches
- Waterproof control systems with IP68 ratings
- Specially designed exhaust and intake systems
- Hermetically-sealed connection points
While significantly more expensive than standard equipment, these specialized systems can operate in flood-prone areas where other options aren't feasible.
Availability Note:
Truly submersible residential generators are limited in availability and typically require custom engineering at substantially higher cost.
Specialized Maintenance for Flood-Zone Generators

Generators in flood-prone areas require specialized maintenance procedures to ensure reliability when needed most:
Preventative Maintenance Focus Areas
- Regular inspection of elevation platforms and anchoring
- Waterproof seals and gasket integrity checks
- Verification of water detection systems
- Testing of automatic shutdown features
- Inspection of flood-resistant conduit and connections
- Evaluation of platform drainage systems
- Assessment of corrosion protection measures
- Checking quick-disconnect systems functionality
Maintenance intervals should be increased for generators in flood-prone areas, with comprehensive checks before flood seasons.
Post-Flood Recovery Procedures
- Professional inspection before reactivation
- Complete electrical system assessment
- Moisture detection in control systems
- Fuel system contamination testing
- Oil and filter replacement regardless of schedule
- Verification of foundation and platform integrity
- Control system diagnostic evaluation
- Generator load bank testing prior to reconnection
Never attempt to restart a generator that has been exposed to flooding without professional inspection.
Pre-Flood Season Checklist
Platform and Installation:
- Inspect platform for cracks or settlement
- Check all mounting bolts and anchors
- Verify drainage systems are clear
- Ensure no erosion around foundation
- Test any sump pumps in generator enclosures
- Confirm appropriate clearances maintained
Electrical and Connectivity:
- Inspect all conduit entries for water intrusion
- Test transfer switch operation
- Verify seals around electrical connections
- Check control panel protection measures
- Test remote monitoring systems
- Confirm emergency contact information is current
Completing this checklist before flood season helps ensure your generator will function when needed most. Consider scheduling professional maintenance to coincide with seasonal flood risk in your area.
Insurance and Recovery Planning

Despite the best placement strategies, flood risks remain. Proper insurance and recovery planning are essential components of comprehensive generator protection:
Generator Flood Insurance Considerations
- Standard homeowners insurance typically excludes flood damage to generators
- FEMA flood insurance may cover permanently installed generators if properly elevated
- Equipment breakdown coverage generally excludes flood-related failures
- Specialized equipment floaters may provide additional protection
- Documentation requirements include installation certifications and elevation compliance
- Compliance with placement standards is often a prerequisite for coverage
Review your insurance policies specifically regarding generator coverage in flood events, as many homeowners discover coverage gaps only after a loss.
Flood Recovery Planning for Generator Systems
- Maintain a list of qualified generator service professionals
- Document your generator specifications and installation details
- Keep records of all flood protection measures implemented
- Establish procedures for safe generator shutdown before flooding
- Develop a plan for temporary power if your generator is damaged
- Consider service contracts that include priority emergency response
- Store essential spare parts above flood levels when possible
A comprehensive recovery plan can significantly reduce downtime if your generator is affected by flooding despite protective measures.
Common Questions About Generator Placement in Flood-Prone Areas
Can I place my generator in a basement or below-grade utility room?
No, placing generators in basements or below-grade areas in flood-prone regions is strongly discouraged for multiple reasons. First, these locations are most vulnerable to flooding, even during minor events. Second, generator exhaust contains deadly carbon monoxide gas that can accumulate in enclosed below-grade spaces. Third, most building codes and FEMA regulations explicitly prohibit placing mechanical equipment below the Base Flood Elevation in designated flood zones. While basement placement might seem convenient for connections and aesthetics, it creates severe safety hazards and virtually guarantees generator damage during flooding events.
How does a flood-optimized generator placement affect installation costs?
Installing generators in flood-prone areas typically increases costs by 25-60% compared to standard installations. The primary cost factors include: (1) Engineered elevation platforms or structural modifications ($800-$5,000); (2) Enhanced electrical connections with waterproof components ($500-$1,200); (3) Additional permit and compliance documentation ($200-$800); (4) Specialized flood-resistant enclosures ($600-$2,000); and (5) Potential engineering assessments ($800-$1,500). While these costs are significant, they should be viewed as an investment in reliability and longevity. The cost of replacing a flood-damaged generator (often $10,000-$20,000) far exceeds the additional expense of proper flood-resistant installation.
What's the best fuel type for generators in flood-prone areas?
Natural gas generally offers advantages for flood-prone installations because: (1) No on-site fuel storage is required, eliminating the risk of fuel contamination or leakage during flooding; (2) Underground gas lines are typically less vulnerable to flood damage than above-ground fuel tanks; (3) Fuel supply automatically resumes when floodwaters recede; and (4) No refueling is necessary during extended operation. However, natural gas may be unavailable in some areas, particularly during major disasters. In such cases, propane with elevated, secured tanks offers a good alternative. Diesel systems require the most extensive flood protection measures due to environmental concerns and fuel quality issues if water contamination occurs. The optimal choice ultimately depends on your specific site conditions and local utility reliability.
Protect Your Generator Investment in Flood-Prone Areas
Proper placement and flood protection measures are essential for generator reliability when you need it most—during severe weather and flooding events.
Related Articles

How to Secure Your Standby Generator Against Theft and Vandalism
Learn how to protect your generator from security threats while maintaining flood protection.

Extreme Weather Generator Operation
Discover how to ensure your generator functions properly during severe weather conditions.
Generator Sizing Calculator: Find Your Perfect Match
Use our interactive tool to determine the right generator size for your flood-prone home.

Power Outage Statistics: Why Home Backup Power is Essential
Learn why reliable backup power is critical in flood-prone regions.
Key Takeaways
- Elevate generators at least 1-2 feet above the Base Flood Elevation (BFE) or local Design Flood Elevation (DFE)
- Consider flood flow dynamics, debris exposure, and soil stability when selecting generator locations
- Protect utility connections including electrical conduits, fuel lines, and control systems
- Different generator types (air-cooled, liquid-cooled, diesel, natural gas) require specific flood protection strategies
- Ensure compliance with FEMA regulations, local floodplain ordinances, and building codes
- Implement enhanced maintenance protocols specifically addressing flood vulnerabilities
- Verify insurance coverage specifically for generator flood damage
- The additional investment in proper flood-zone placement typically pays for itself by preventing a single instance of major flood damage
- Use our Generator Sizing Calculator to determine the right generator capacity for your flood-resistant installation

