
DIY Generator Maintenance: What You Can Do vs. When to Call a Pro
Published: April 10, 2025 | By Robert Johnson, Certified Generator Technician
A well-maintained generator is a reliable generator. Regular maintenance not only extends your generator's lifespan but also ensures it will perform when you need it most—during a power outage. While some maintenance tasks require professional expertise, many routine procedures can be safely performed by homeowners with basic mechanical skills.
This comprehensive guide will help you understand which maintenance tasks you can handle yourself and when it's time to call in a professional. By following these recommendations, you'll save money on service calls while keeping your generator in optimal condition for years to come.
Key Takeaway: Homeowners can safely perform visual inspections, oil and air filter changes, battery maintenance, and scheduled exercise tests. However, fuel system repairs, electrical adjustments, major engine work, and annual professional servicing should be left to certified technicians. Following the manufacturer's maintenance schedule is essential for warranty protection and reliable operation.
Understanding Maintenance Needs by Generator Type
Different generator types have distinct maintenance requirements. Understanding your specific generator will help you develop an appropriate maintenance strategy:
Standby Generators
Permanently installed whole-house generators require:
- More frequent oil changes (typically every 50-200 operating hours)
- Regular monitoring of coolant levels (for liquid-cooled models)
- Battery maintenance for auto-start functionality
- Software updates and control panel testing
- Transfer switch inspection and testing
These systems typically have automatic self-test features but still require regular human inspection and maintenance.
Portable Generators
Mobile generators used for occasional backup have different needs:
- Fuel stabilization for long-term storage
- More attention to cleaning as they're exposed to diverse environments
- Regular but less frequent oil changes (every 50-100 operating hours)
- Manual exercise schedule since they lack auto-test features
- Carburetor maintenance for proper starting
Portable units often sit unused for long periods, making proper storage and fuel management critical.
For more detailed information on different generator types, see our guide to standby vs. portable vs. inverter generators, which covers their operational differences.


Left: Permanent standby generator. Right: Portable backup generator. Each type has different maintenance requirements.
Generator Maintenance Tasks You Can Safely Do Yourself
These tasks can be performed by most homeowners with basic tools and mechanical skills. Always consult your owner's manual for model-specific instructions and safety procedures.
1. Visual Inspections (Monthly)
What to Do:
- Check for oil/fluid leaks under the generator
- Inspect air intake vents for blockages
- Look for rodent/insect nests and debris
- Verify that nothing has been placed against the unit
- Check for visible damage to outer enclosure
- Ensure exhaust path remains clear
Tools Needed:
- Flashlight
- Work gloves
- Camera (for documentation)
Safety Tips:
- Ensure generator is not running
- Disconnect from power source if possible
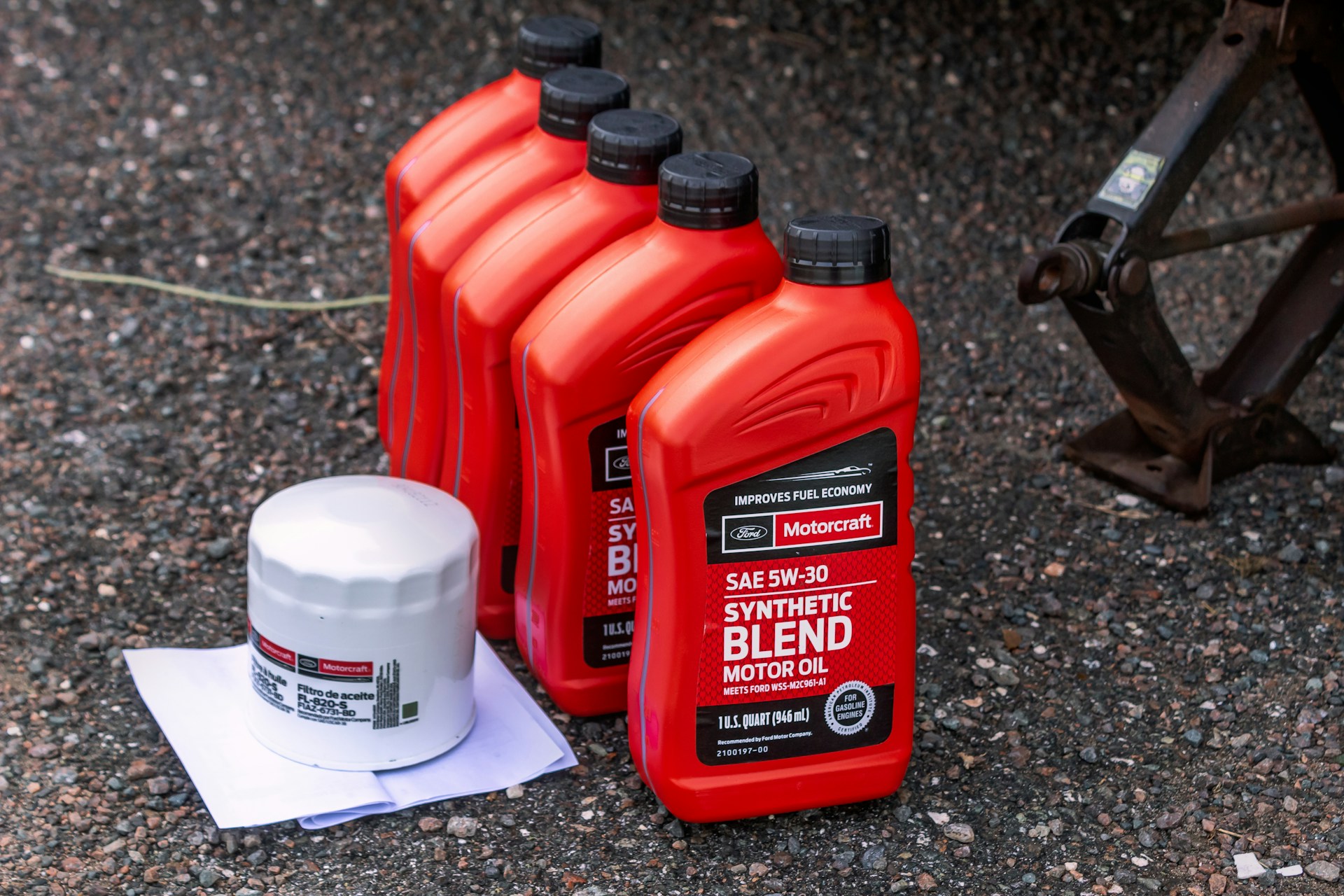
2. Oil Level Checks and Changes
What to Do:
- Check oil levels monthly using dipstick
- Change oil according to schedule (typically every 50-200 operating hours)
- Replace oil filter during oil changes
- Use manufacturer-recommended oil type
- Document oil changes for warranty purposes
Tools Needed:
- Proper weight oil (check manual)
- Oil filter wrench
- Drain pan
- Funnel
- Rags or paper towels
- Oil filter
Safety Tips:
- Allow engine to cool before changing oil
- Dispose of used oil properly
- Clean up any spills immediately
Note: Some standby generators have extended oil change intervals when using synthetic oil. Check your owner's manual for specific recommendations.

3. Air Filter Cleaning & Replacement
What to Do:
- Locate the air filter housing (consult manual)
- Remove and inspect the filter
- Clean foam pre-filters if applicable
- Replace paper elements that are dirty
- Ensure proper reassembly
- Check every 25 operating hours; replace annually or when dirty
Tools Needed:
- Screwdriver (typically Phillips)
- Replacement air filter
- Compressed air (optional for cleaning)
- Clean cloth
Safety Tips:
- Never run generator without air filter
- Don't use petroleum solvents on foam elements
- Ensure filter housing is properly sealed
4. Battery Maintenance
What to Do:
- Clean battery terminals of corrosion
- Check cable connections for tightness
- Apply terminal protectant
- For non-sealed batteries, check electrolyte levels
- Test battery voltage (should be 12.5-13.2V when not charging)
- Replace battery every 2-3 years proactively
Tools Needed:
- Battery terminal cleaner
- Terminal protectant spray
- Wrenches for terminal connections
- Voltmeter
- Baking soda & water solution (for cleaning)
- Gloves and eye protection
Safety Tips:
- Disconnect negative terminal first
- Connect negative terminal last
- Avoid shorting terminals with tools
- Handle batteries carefully
5. Cooling System Inspection
What to Do:
- Clean exterior cooling fins with soft brush
- Remove debris from cooling intakes
- Check coolant level in liquid-cooled models
- Inspect radiator hoses for cracks or leaks
- Ensure fan shroud is secure and undamaged
Tools Needed:
- Soft brush
- Shop vacuum
- Compressed air (low pressure)
- Coolant (for liquid-cooled units)
Safety Tips:
- Always ensure the generator is cool
- Never remove radiator cap when hot
- Use protective gloves and eyewear
6. Scheduled Exercise Tests
What to Do:
- Run generator manually if it lacks auto-exercise
- Verify automatic exercise is working properly
- Listen for unusual sounds during operation
- Monitor oil pressure and temperature gauges
- Check for proper voltage output (if meter available)
- Ensure unit shuts down properly after test
Tools Needed:
- Owner's manual
- Notebook for recording observations
- Multimeter (optional)
Safety Tips:
- Maintain safe distance during operation
- Never touch electrical connections
- Be aware of exhaust direction
For standby generators, most manufacturers recommend weekly auto-exercise periods of 20-30 minutes under load.
Beyond these tasks, homeowners should also keep the area around the generator clear of debris, vegetation, and snow to ensure proper ventilation and reduce fire hazards.
Your DIY Generator Maintenance Schedule
Follow this schedule to keep your generator in optimal condition. Adapt the time intervals based on your specific model's requirements and usage patterns:
| Maintenance Task | Portable Generators | Standby Generators | Skill Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Before each use | Monthly | Beginner |
| Check Oil Level | Before each use | Monthly | Beginner |
| Oil Change | Every 50-100 hours or annually | Every 50-200 hours or annually | Intermediate |
| Air Filter Inspection | Every 25 hours of use | Every 25 hours or quarterly | Beginner |
| Battery Maintenance | Every 3 months (if equipped) | Every 3 months | Intermediate |
| Clean Cooling Fins | Every 100 hours or annually | Every 100 hours or annually | Intermediate |
| Exercise Test | Every 30 days (manual) | Weekly (usually automatic) | Beginner |
| Spark Plug Inspection | Every 100 hours | Annually (professional) | Intermediate |
| Fuel System Check | Every 6 months | Annually (professional) | Professional |
| Complete Tune-Up | Annually | Annually | Professional |
Remember that adhering to the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule is essential for preserving warranty coverage. For more details on maintaining your generator for different seasons, see our guide on winter generator preparation.

Regular testing and inspection of your generator's transfer switch is an important part of a comprehensive maintenance program
When to Call a Professional: Tasks Best Left to the Experts
While DIY maintenance is possible for many routine tasks, some generator work should be performed only by certified technicians. Attempting these tasks without proper training could void your warranty, damage your equipment, or create safety hazards.
1. Fuel System Repairs and Adjustments
Professional service is required for:
- Carburetor adjustment, cleaning, or rebuilding
- Fuel injector service or replacement
- Fuel pump repairs
- Fuel line replacements
- Gas pressure adjustments (for natural gas/propane systems)
- Fuel system leak diagnosis and repair
Why call a pro: Fuel system components require precise adjustment and specialized tools. Improper work can create fire hazards or damage sensitive components.
2. Electrical System Service
Leave these electrical tasks to professionals:
- Transfer switch installation or repair
- Control panel troubleshooting
- Voltage regulator adjustment or replacement
- Circuit board repairs
- Generator output testing and adjustment
- Rewiring or connection changes
- Software/firmware updates
Why call a pro: Electrical work carries shock hazards and requires specialized equipment for testing. Incorrect adjustments can damage your home's electrical system or the generator itself.
3. Engine Internal Repairs
These tasks require professional expertise:
- Valve adjustments
- Head gasket replacement
- Piston ring service
- Cylinder honing or repair
- Crankshaft or camshaft work
- Engine timing adjustments
- Governor adjustments
Why call a pro: Internal engine work requires specialized tools, precise measurements, and extensive mechanical knowledge. Improper repairs can lead to catastrophic engine failure.
4. Annual Professional Service
Even with regular DIY maintenance, your generator should receive annual professional service to include:
- Comprehensive load bank testing
- Exhaust system integrity check
- Fuel pressure testing and adjustment
- Full electronic diagnostic scan
- Transfer switch operation verification
- Control system testing and calibration
- Complete emissions testing
Why call a pro: Professional service verifies overall system health, uncovers potential problems before they cause failures, and ensures all components are working together properly. This service is typically required to maintain warranty coverage.
5. Troubleshooting Performance Problems
Contact a professional when you experience:
- Generator fails to start or starts then stalls
- Unusual noises during operation
- Visible smoke from exhaust (beyond normal startup)
- Circuit breakers that trip repeatedly
- Erratic voltage output or flickering lights
- Error codes on the control panel
- Coolant or oil leaks
Why call a pro: Diagnosing complex issues requires specialized diagnostic equipment and systematic testing procedures. Professional technicians can efficiently identify root causes rather than just treating symptoms.
Remember that proper generator maintenance requires a partnership between homeowner vigilance and professional expertise. Regular DIY maintenance combined with annual professional service provides the best protection for your investment.
Finding Qualified Generator Service Technicians
Not all service providers are equally qualified to work on generators. When selecting a professional for maintenance or repairs, look for these qualifications:
What to Look For
- Manufacturer certification for your specific generator brand
- EGSA certification (Electrical Generating Systems Association)
- Master electrician license for transfer switch/electrical work
- Specific generator training credentials from recognized programs
- Proof of insurance including liability coverage
- Local business history with verifiable references
- Emergency service availability for critical failures
Questions to Ask
- How many years have you been servicing my generator brand?
- Are your technicians factory-trained and certified?
- What diagnostic equipment do you use?
- Do you offer service contracts with priority scheduling?
- Will service be documented for warranty purposes?
- Do you stock common parts for my generator model?
- What is your response time during emergencies?
For help finding qualified professionals in your area, use our generator service technician directory to connect with pre-screened experts who specialize in your specific generator brand and model.
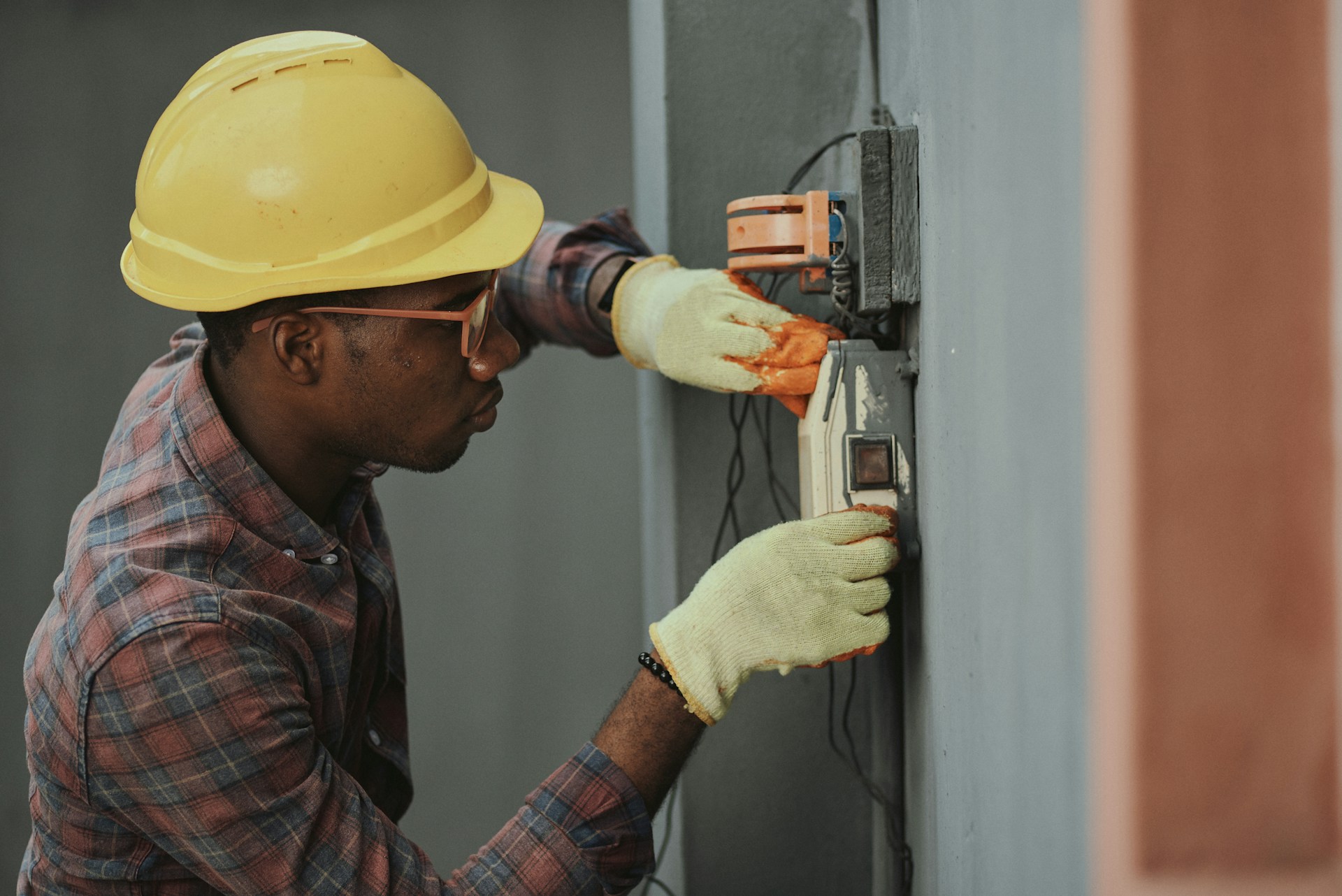

A certified generator technician has specialized tools and training for complex maintenance tasks
Safety First: Essential Precautions for DIY Maintenance
Regardless of which maintenance tasks you undertake yourself, always follow these critical safety precautions:
Generator Maintenance Safety Checklist
- Always disable the generator before maintenance - Disconnect battery, remove spark plug wire, or use the shutdown procedure specified in your manual
- Wait for complete cooling - Allow at least 30 minutes after operation before servicing to prevent burns
- Prevent accidental starting - For standby generators, disable automatic start features and place in "OFF/MAINTENANCE" mode
- Maintain ventilation - Never run a generator for testing in enclosed or partially enclosed spaces
- Use appropriate safety gear - Gloves, eye protection, and hearing protection when needed
- Prevent fuel hazards - No smoking, open flames, or sparks when working with fuel systems
- Lift properly - Use appropriate lifting techniques and get help for heavy components
- Document your work - Keep records of all maintenance performed
- Consult the manual - Always refer to manufacturer guidelines for your specific model
Remember that your safety is always more important than completing a maintenance task. If you encounter any situation where you're unsure of the proper procedure or don't have the right tools, it's better to stop and consult a professional.
Common Questions About Generator Maintenance
How often should I change my generator's oil?
For portable generators, change the oil every 50-100 operating hours or at least once annually, whichever comes first. For standby generators, follow the manufacturer's recommendation, which typically ranges from 50-200 operating hours depending on the model and oil type. When using synthetic oil, extended intervals may be permitted. Always check your owner's manual for the specific requirements of your generator.
What happens if I don't maintain my generator regularly?
Neglected generators experience significantly higher failure rates precisely when you need them most—during power outages. Common issues from poor maintenance include starting failures, reduced power output, premature component wear, and potentially catastrophic engine damage. Additionally, most generator warranties require proof of regular maintenance, so neglect can void your warranty coverage, leaving you responsible for costly repairs.
Can I use synthetic oil in my generator?
Yes, most generators can use synthetic oil, and many manufacturers now recommend it. Synthetic oil typically offers better performance in extreme temperatures, extended change intervals, and improved engine protection. However, you must still use the correct viscosity grade (such as 5W-30, 10W-30, etc.) specified for your generator model. Check your owner's manual for specific recommendations, as some older generators may have limitations on synthetic oil use.
How much does professional generator maintenance cost?
Annual professional service for residential generators typically costs between $200-$500 depending on your location, generator size, and the specific services included. Basic maintenance visits focusing on inspection and oil change fall at the lower end, while comprehensive service including load bank testing, full diagnostics, and filter replacements will be at the higher end. Many service providers offer maintenance contracts with scheduled visits at reduced rates, which can be more economical long-term while ensuring regular service.
Keep Your Generator Ready When You Need It
Proper maintenance ensures your generator will perform reliably during power outages. Whether you're handling routine maintenance yourself or need professional service, we can help.
Related Articles

Generator Maintenance Checklist
Detailed monthly and annual maintenance tasks to keep your generator in peak condition.

How to Prepare Your Generator for Winter
Special maintenance considerations for cold weather operation and storage.

How Long Do Whole-House Generators Last?
Learn how proper maintenance can extend your generator's lifespan and reliability.

Gas vs. Propane vs. Diesel: Which Fuel Type is Best?
Understand the maintenance requirements for different generator fuel types.
Key Takeaways
- DIY-friendly tasks include visual inspections, oil/filter changes, battery maintenance, and scheduled testing
- Professional service is required for fuel system work, electrical adjustments, internal engine repairs, and annual comprehensive maintenance
- Following the manufacturer's maintenance schedule is essential for warranty protection and reliable operation
- Different generator types (portable vs. standby) have distinct maintenance requirements and schedules
- Proper safety precautions are critical when performing any generator maintenance
- Keeping detailed maintenance records helps track service history and maintain warranty coverage
- Using qualified, certified technicians for professional service ensures proper care and protects your investment

